Advances in Animal and Veterinary Sciences
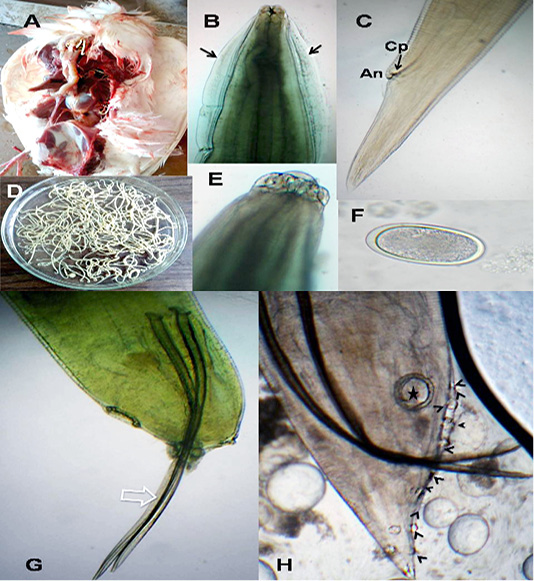
A. galli. A)Macrophoto of Ascaridia species in pigeon intestine; B) A. galli anterior end with cervical alae (arrows); C) Female tip tail with anus (An) and one pair of caudal papillae (Cp); D)Macrophoto of Ascaridia species; E) trilobed lips of A. galli; F) A. galli egg; G&H) Male caudal end of A. galli (large arrow: spicules, star: precloacal sucker, arrow heads: caudal papillae). (Digital camera)
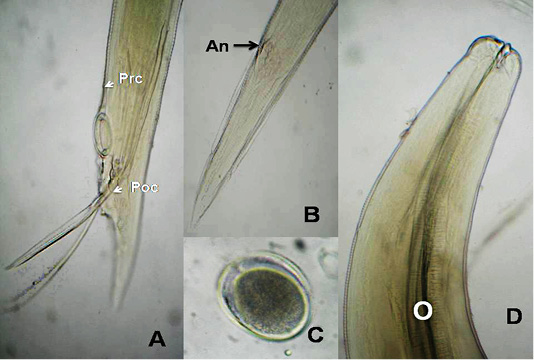
A. columbae, A) Male caudal end of (Prc: precloacal papillae, Poc: postcloacal papillae); B) Female tip tail with anus (An); C)egg; D) anterior end with club-shaped esophagus (O). (Digital camera)
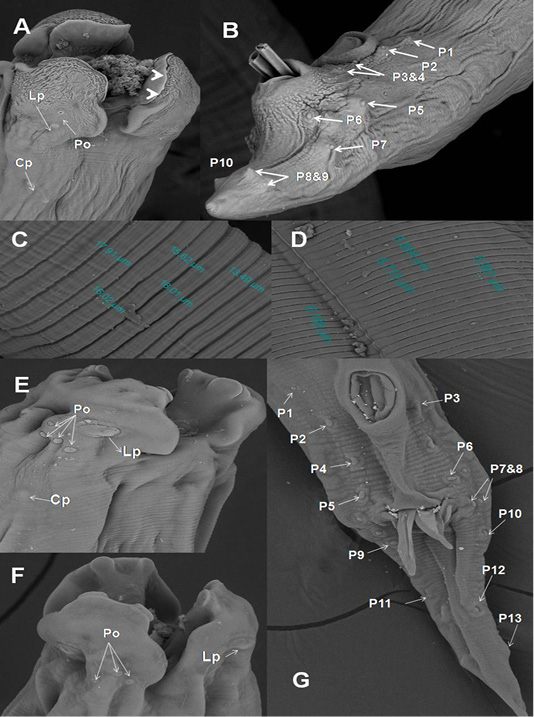
SEM of A. galli and A. columbae. A) Onion exposed A. galli anterior end with cuticular shrinkage of trilobed lips provided with inner 2 tooth-like projections (arrow heads). Also, oral cavity filled with granulation tissue and loss some of amphidial pores (2000x); B) Male caudal end of A. galli provided with cuticular vesicles and carried ten pairs of caudal papillae (800x);C)Wider A. galli cuticular transverse striation divided by subannuli (1600x);D) Wide A. columbae cuticular transverse striation (1600x); E&F) A. columbae trilobed lips carried triangular teeth, labial papillae, amphidial pores and cervical papillae (3000x); G) Male caudal end of A. columbae carried thirteen pairs of caudal papillae (1000x). Abbreviations: labial papillae (Lb), amphidial pores (Po), cervical papillae: (Cp) and caudal papillae (p1-p13).
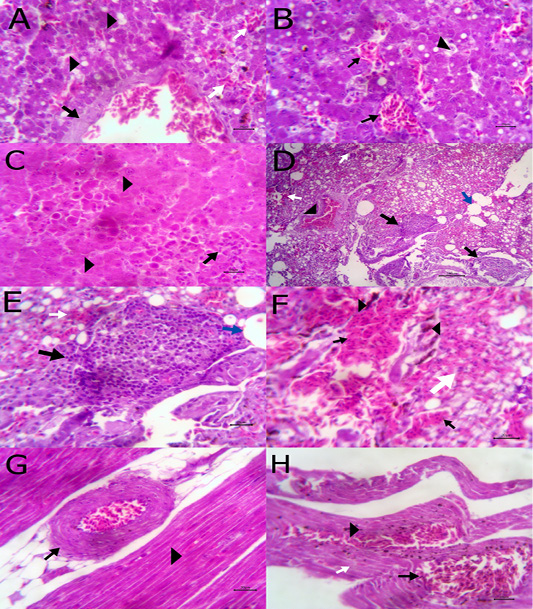
A) Liver showing congestion of central vein with mild thickening of its wall (arrow) and fatty degeneration (arrow head, bare=20); B) Liver showing telangectiasis of hepatic sinusoids (arrow) beside fatty degeneration (arrow head, bare=20); C) Liver showing coagulative necrosis among hepatic cells (arrow head) and aggregation of polymorphic inflammatory cells (arrow, bare=20); D) Lung showing follicular bronchitis(black arrow), hemorrhage among the alveoli (white arrow) and emphysematous alveoli (blue arrow, bare=100); E) Higher magnification of the previous figure to show hyperplasia of lymphoid follicles (black arrow), hemorrhage (white arrow) and emphysematous alveoli (blue arrow, bare=20); F) Lung showing thickening of interalveolar septa by extravasated erythrocytes (arrow) beside hemosiderosis(arrow head)and leukocytic infiltrations (white arrow) bare=20; G) Heart showing mild hyaline degeneration of the myocardial muscle (arrow head) beside congestion of blood vessels with hyaline thickening of its wall and perivascular edema (arrow, bare=20); H) Heart showing extravasated erythrocytes (arrow) among degenerated muscle fibers (white arrow) with hemosiderosis (arrow head, bare=20).
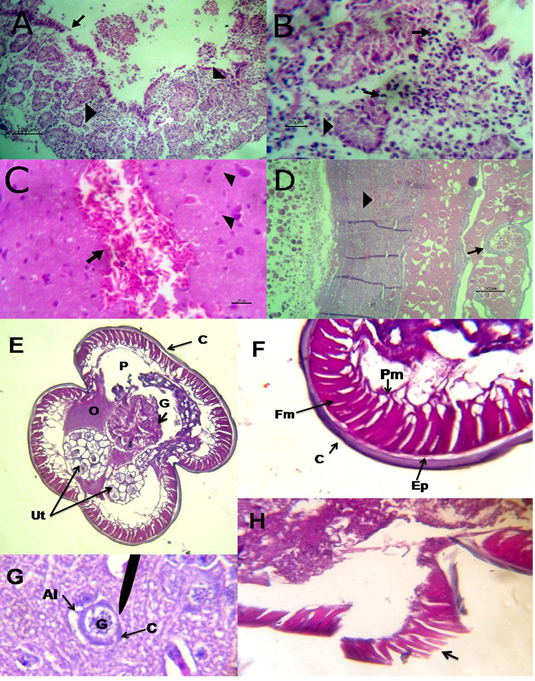
A) Intestine showing necrosis of intestinal mucosa with desqumation of lining epithelium inside the lumen (arrow) beside eosinophils aggregations in the lamina propria (arrow head) among necrotic gland (white arrow, bare=100); B) Higher magnification of the previous figure to show aggregations of eosinophils (arrow) among necrotic glands (arrow head, bare=20); C) Brain revealing extravasated erythrocytes (arrow) beside degeneration of some neurons (arrow head, bare=20); D) Ovary revealing congestion of ovarian blood vessel (arrow) and extravasated erythrocytes inside ovarian stroma (arrow head, bare=100); E)Cross section of A. galli contained uterus (Ut), ovary (O) and gut (G) inside the peudocel (P) covered by body wall; F) body wall consisted of cuticle (C), epidermal layer (Ep), fibrillar (Fm) and proplasmic muscle (Pm) components; G) A. galli larva cross section in liver contained gut (G) covered by cuticle (C) with prominent alae (Al);H) Damage of the cuticle and epidermal layer (arrow) exposed to chopped green onion. (Digital camera)